Vitamin K2
Wij zeggen het al een tijdje maar onlangs kwamen wij op youtube een aantal videos tegen over vitamine K2. Hierin komt Professor Vermeer van de Universiteit van Maastricht aan het woord met een zeer opgetogen relaas over Vitamine K2. Het wordt nog net geen wondermiddel genoemd.
The first clip is from the Limburg broadcasting company L1, from the programme Limburg laat:
And RTL7 also paid attention to it:
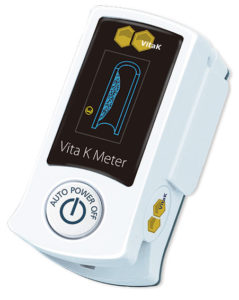
The Vita-K meter of Professor Vermeer
To be able to say something about the condition of the blood vessels and the vitamin K in the body, Cees Vermeer founded a company to develop simple measurements: the Vita-K meter.
Relation COVID-19 and vitamin K deficiency
Free Vita-K measurement with every consultation of Thermography Amsterdam
Wat te doen bij teveel calcium?
Op YouTube kun je ondertitels vinden door naar de video te gaan die je wilt bekijken en te kijken of er een ondertitel-icoon beschikbaar is. Dit icoon bevindt zich meestal rechtsonderin de video, naast de instellingen-knop (een tandwiel).
Want to know more about the Vita-K measurement and what it actually measures?
Read more here
Click Here
The average intake of vitamin K2-which we get from our diet-has declined significantly over the past 50 years.
The Rotterdam study in 2004 was a 10-year study with over 4500 participants.
had significantly less calcium in their blood vessels.
It was concluded that about 90% of the participants were deficient in vitamin K2.
Vitamin K2 is beneficial for:
- De botten, Met extra inname van vitamine K kan zelfs osteoporosis worden voorkomen!!
- Cardiovascular by reducing arteriosclerosis, vitamin K2 plays a key role in the prevention of arterial calcification.
- Insulin resistance and inhibition of diabetes (Blood glucose levels regulation by carboxylated osteocalcin and the anti-inflammatory effect).
- Joint inflammation (Inhibition of various pro-inflammatory substances such as COX-2, prostaglins type 2).
- Lowering of cholesterol levels
- Inhibition of plaque formation such as AGEs. (advanced glycation end products)
- Inhibition of rheumatism and arthritis.
- Inhibitory in age-related diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases, the progression of Alzheimer's disease and incipient dementia.
Een belangrijke functie van vitamine K is het activeren van de Gla-eiwitten, die samen met vitamine D de calciumhuishouding reguleren en verkalking van zachte weefsels als ook de borsten en botontkalking of wel osteoporoses counteracts.
Through the diet, we get vitamin K1 in particular from green leafy vegetables.
The function of vitamin K is to activate GLA protein, the inhibitor of calcium deposition in soft tissue.
Vitamin K2 is een groep van menaquinonen wordt geproduceerd door bepaalde bacteriën en komt in beperkte mate voor in vlees, zuivel en eieren.
Vitamins K2 is transported with LDL (just like vitamin E).
- Vitamin C enhances the anticancer activity of vitamin K.
Vitamin K deficiencies, in addition to not eating, can be caused by:
- Liver disease, cystic fibrosis.
- Gal problemen of het ontbreken van een Gal. Het is namelijk een vet-oplosbare vitamine)
- Bij darmproblemen als: chronische diarree, coeliakie, ziekte van Crohn, colitis ulcerosa, short bowel syndrome, intestinale resectie (met name laatste deel van het ileum),
- After a stomach reduction
- medication such as antibiotics and aspirin.
- Alcoholism
- Overweight
- Vitamin A and E (in hoge doseringen) kunnen de vitamine K verlagen.
Be aware that also Q10 also has vitamin K2-like effects as an interaction with blood thinners. Use of both drugs with blood thinners increases the risk of blood thickening.
BE CAREFUL IF YOU'RE ON BLOOD THINNERS.
Vitamine K-antagonisten zijn een klasse van antistollingsmiddelen die de werking van vitamine K blokkeren, waardoor de productie van bepaalde stollingsfactoren in het bloed wordt verminderd. Enkele voorbeelden van vitamine K-antagonisten zijn:
- Warfarine (Coumadin)
- Acenocoumarol (Sintrom)
- Fenprocoumon (Marcoumar)
Het is belangrijk om op te merken dat er ook andere antistollingsmiddelen beschikbaar zijn die niet tot de categorie van vitamine K-antagonisten behoren, zoals de directe orale anticoagulantia (DOAC’s).
Then K2 should only be used under medical supervision.
- Vitamin K supplementation reduces the effectiveness of vitamin K antagonists such as blood thinners like warfarin. Use of these medications requires medical supervision at doses of vitamin K above 100 mcg per day.
- The use of vitamin K antagonists (blood thinners such as warfarin) is associated with increased calcification of the heart valve and coronary arteries.
There are many studies on vitamin K2. Here are some:
Food and Nutrition Board, Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc. Washington, DC: National Academy Press, 2002. Available at: www.nap.edu/books/0309072794/html/.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15961706/
Relation of oral anticoagulation to cardiac valvular and coronary calcium assessed by multislice spiral computed tomography
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16169351/
Regression of warfarin-induced medial elastocalcinosis by high intake of vitamin K in rats
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17138823/
Vitamin K status and bone mass in women with and without aortic atherosclerosis: a population-based study
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8849401/
A comprehensive review of vitamin K and vitamin K antagonists
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10806559/
High dietary menaquinone intake is associated with reduced coronary calcification
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18722618/
Anti-arthritis effects of vitamin K(2) (menaquinone-4)-a new potential therapeutic strategy for rheumatoid arthritis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17681015/
Age- and brain region-specific effects of dietary vitamin K on myelin sulfatides
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20092997/
Patients with unstable control have a poorer dietary intake of vitamin K compared to patients with stable control of anticoagulation
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15886802/
Dietary Reference Intakes for vitamins A and K, iron, iodine, chromium, copper, manganese, molybdenum, zinc, and other potentially beneficial trace elements such as boron to determine the roles, if any, they play in health.

